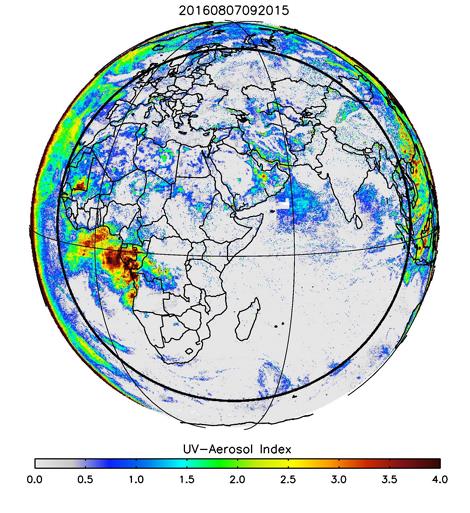
Aerosol Index

The UV Aerosol Index (UVAI) is a measure of the satellite observed change in spectral contrast of upwelling reflectances at two near-UV wavelengths in relation to the calculated spectral contrast of a pure molecular atmosphere. The EPIC UVAI is derived from reflectance measurements at 340 and 388 nm, from the expression
UVAI = -100 [ log10 (I388/I340)measured - log10 (I388/I340)calculated ]
Non-zero UVAI values are associated with wavelength dependent radiative transfer effects unaccounted for in the calculations. Reflection by land and ocean surfaces, as well as clouds and aerosols scattering yield small negative and positive values, whereas absorption by desert dust, carbonaceous aerosols, and volcanic ash are associated with UVAI values larger than 1.0. The UVAI magnitude depends mainly on aerosol optical depth, the spectral dependence of particle absorption (or Aerosol Absorption Exponent), and the height of the aerosol layer.
The two images below are examples of dust and smoke observed flowing from Africa, with the smoke coming from agricultural biomass burning.